-
Themes in Chemistry - Pacing Guide - 2024-2025
Chemistry is the study of matter and its interactions. In this course students will explore and answer the following questions as they learn about key ideas in chemistry:
-
How can one explain the structure and properties of matter?
-
How do substances combine or change (react) to make new substances?
-
How does one characterize and explain these reactions and make predictions about them?
-
What role does energy play in chemical reactions?
Participants will explore three different levels of chemistry understanding: macroscopic (observation based), particulate (what is going on at the level of atoms), and symbolic (written representations).
The text for this course is “Active Chemistry”. Students will check out the book at orientation.
Quarter
Unit
Primary Focus / Chemistry Topics
1
Ch 1 - Movie Special Effects - Create a movie scene in which you produce special effects incorporating the chemistry you have learned.
-
How does chemistry relate to moviemaking?
-
How can you predict the behavior of elements, compounds and molecules in order to use them in special effects?
Safety
Elements & Compounds
States of Matter
Solutions, Suspensions and Colloids
Physical Properties of Matter
Density - Measuring Mass and Volume
Properties of Metals and Non-metals
Polymers - Natural and Synthetic
Flame Tests - Identifying Metals
Organic Compounds and Combustion
1-2
Ch 6 - Cool Chemistry Show - Demonstrate and explain chemistry concepts to other students.
-
How can changes in matter be demonstrated in an exciting way?
-
How does matter change?
-
How can chemical change be expressed in writing?
-
How can chemical change be classified?
-
Why does chemical change occur?
Solutions: Chemical or Physical Change?
Characteristics of a Chemical Change
Chemical Names and Formulas
Reaction Types and Chemical Equations
Reaction Diagrams and Conservation of Energy
Factors in Reaction Rates
Acids, Bases and Indicators - Colorful Chemistry
Oxidation and Reduction of Metals
2
Ch 3 - Artist as Chemist - Create a work of art that expresses yourself and to create a museum display explaining the chemistry around your artwork.
-
What makes something art?
-
What determines properties of matter?
-
How can we use the predictable nature of matter to produce art works?
Acid-Base Chemistry
Chemical Properties of Metals
Physical Properties of Metals
From Hydrate to Anhydrate: Percentage Composition
Solubility Rules: Paints and Precipitates
Natural Dyes, pH and Mordants
Metal Oxides: How does Stained Glass Get its Color?
3
Ch 2 - Fun with the Periodic Table - Develop a game (card? computer? board? other?) that can be used to teach others how to learn and use the periodic table.
-
What is the purpose of models? How do they change over time?
-
How does the structure of atoms affect their function and properties?
-
How can you creat an organization chart to assist in understanding?
-
How do you investigate things you cannot see?
Periodicity and Trends: Organizing a Store
Elements and Their Properties
Atomic Theory and Atomic Mass
Parts of the Atom - Electrons and the Nucleus
Line Spectra and Atomic “Jumps”
Ionization Energy and Orbitals
Noble Gases as a Key to Chemical Behavior
The Octect Rule and Bonding
Nuclear Forces: What limits and Determines an Atom’s Mass?
3-4
Ch 4 - Chemical Dominos - Create a prototype of a “chemical-dominoes sequence” that can be sold by a toy company to 10-15 year old children. You will demonstrate the product and explain the chemistry concepts behind each step.
-
How do you design a robust and repeatable process that makes something?
-
How do you control the direction a change will take?
-
How can you take advantage of knowledge of a material’s properties to make the material do something?
Energy and Entropy: Alternative Reaction Pathways
Balancing Chemical Equations
Stoichiometry: How much gas is produced?
The Metal Activity Series: What Can Destroy a Metal/
Visible Light, Energy, and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electrochemical Cells and Half-Reactions
Enthalpy: Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Entropy and Enthalpy: Changes in a Rubber Band
4
Ch 7 - Cookin’ Chem - Create a segment of a television cooking show that explains in detail the chemistry behind the cooking involved.
-
What kind of chemistry is involved in cooking?
-
What safety issues are common to chemistry and cooking?
-
How can cool acids “cook” foods?
-
What happens to food when we cook it?
-
Why do we need so many types of pots and pans?
-
What is unique about the shape of a soap molecule?
Heat Transfer: What is Heat?
Combustion Reactions and Hydrocarbons
Thermochemistry and Cooking Fuels
Phase Changes and the Heating Curve of Water
Phase Changes and the Cooling Curve of Water
Calorimetry and Specific Heat Capacity
Denaturation: How do Proteins in Foods Change?
Modeling Organic Molecules: Soap
Note: The text includes several other units, which we are unlikely to have time to learn about. They are:
Ch 5 - Ideal Toy - create a toy that operates on chemical and/or gas principles.
Ch 8 - CSI Chemistry - create a crime scene and prepare evidence that requires the use of at least three forensic chemistry techniques.
Notes: The units and their pacing are always being refined and updated and are subject to change. This document will be updated periodically. If you have questions, comments, or concerns, please contact Ms. Sandy (sandra.smith@CO01900838.schoolwires.net)
FHAP - Themes in Science Courses
This FHAP Themes in Chemistry class is delivered twice per week (Tuesday AND Thursday) in a unit-studies format. During class, students will have the opportunity to explore and discover science in an active, collaborative and creative way. In addition to the classroom activities, students are expected to complete related homework assignments generally due each Tuesday or Thursday before (8am) or at the beginning of the science class. Students who are actively participating in both classwork and homework can considered this course as a full year of science study and parents may assign a full credit to their student’s transcript as desired.
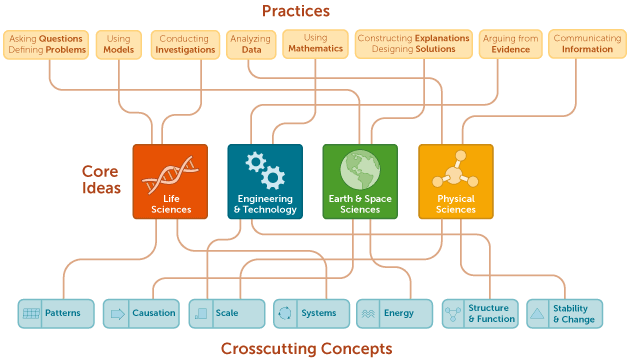
The content of all FHaP science courses will be drawn from key ideas in science that have broad importance within or across multiple science disciplines, including Physical Science, Life science, and Earth and Space Science. Themes in Chemistry is classified as a physical science course. In addition to the science content, the science classes will integrate crosscutting science principles as opportunities arise. Students will engage in science practices to build, deepen, and apply their knowledge of key ideas and crosscutting concepts. The graphic on the next page gives an overview of this information.
Re: KEY IDEAS: Students in the Themes in Chemistry course will learn about the following key ideas found in the Colorado 2020 Science Standards:
1. The subatomic structural model and interactions between electric charges at the atomic scale can be used to explain the structure and interactions of matter.
2. Chemical processes, their rates, their outcomes, and whether energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of collisions of molecules, rearrangement of atoms, and changes in energy as determined by properties of elements involved.
3. The strong nuclear interaction provides the primary force that holds nuclei together. Nuclear processes including fusion, fission, and radioactive decays of unstable nuclei involve changes in nuclear binding energies.
Re: CROSS CUTTING SCIENCE PRINCIPLES :
Patterns, Causation, Scale, Systems, Energy, Structure & Function, Stability & Change
Re: SCIENCE PRACTICES :
Asking Questions, Using Models, Conducting Investigations, Analyzing Data, Using Mathematics, Constructing Explanations, Arguing from Evidence, Communicating Information
-
Select a School...
Select a School
- Falcon High School
- Falcon Middle School
- Falcon Elementary School of Technology
- Meridian Ranch Elementary School
- Woodmen Hills Elementary School
- Bennett Ranch Elementary School
- Vista Ridge High School
- Skyview Middle School
- Odyssey Elementary School
- Inspiration View Elementary School
- Ridgeview Elementary School
- Academy for Literacy, Learning & Innovation Excellence
- Sand Creek High School
- Horizon Middle School
- Evans Elementary School
- Remington Elementary School
- Springs Ranch Elementary School
- Stetson Elementary School
- Falcon Homeschool Program
- Patriot High School
- Pikes Peak Early College
- Springs Studio For Academic Excellence
- Team Website